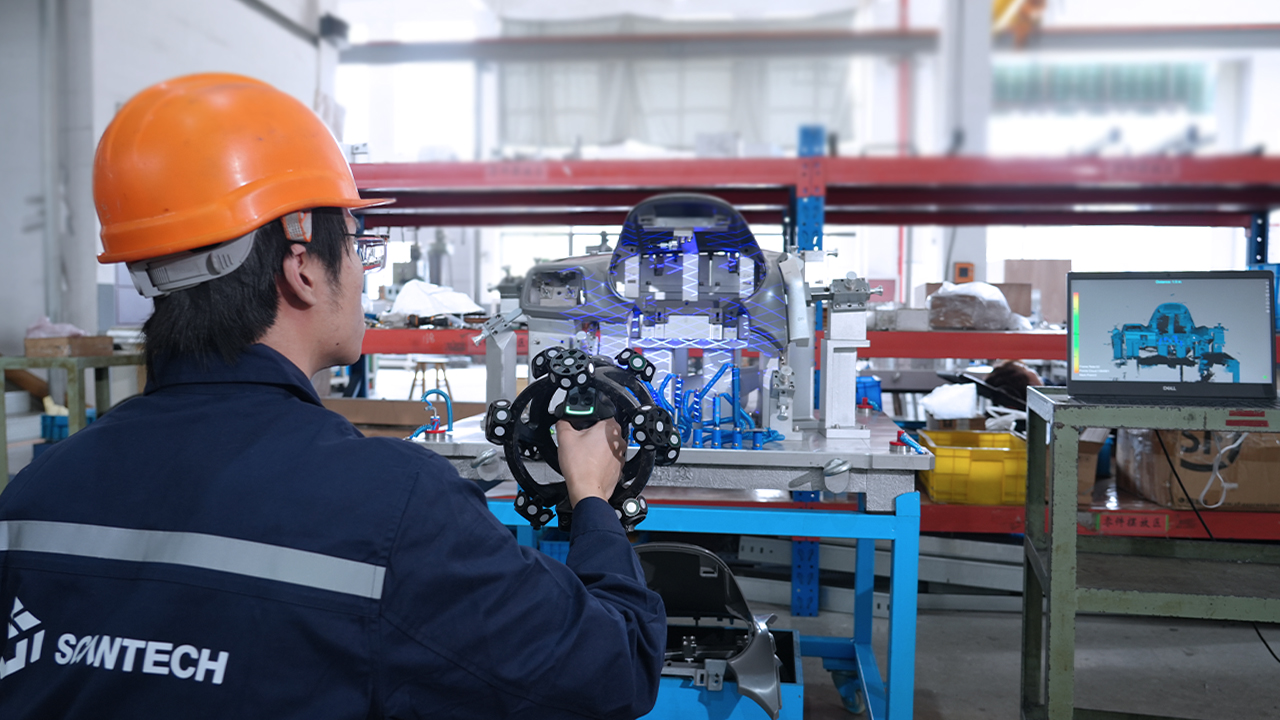
Selecting a 3D scanner can feel like buying a car or a house. Get it right, and everything goes smoothly. Get it wrong, and you could waste time and your budget on a purchase that’s not right for your needs. It’s not that either Artec or SCANTECH is better – it all just depends on what you’re using it for.
3D scanning offers multiple benefits:
- Speeding up data capture and measurement processes
- Gaining instant feedback on elements that need more data
- Collaborating between departments and creating digital twins
- Reverse engineering and recreating legacy parts
- Improving accuracy to reduce guesswork and maximize inspections
In this article, we take the mystery out of how to choose the right scanner for your needs by giving you the top five things to look for when buying a 3D scanner.
Then, we hone in on the features of SCANTECH versus Artec 3D scanners, as for many companies, it often comes down to a choice between the two. Is one better than the other? That depends on your industry, scanning applications, and where the scanner will be used. Some organizations even discover that both are what they need.
Armed with this information and a strategy for assessing your unique requirements, you can be confident about your final 3D scanner selection.
Selecting the Right 3D Scanner

For most businesses, choosing the best 3D scanner starts with determining where it will fit into their workflow.
Use these six questions to help you address this issue:
- Do you often get parts without drawings from third parties?
- Is hand measuring and creating CAD models a time-consuming task?
- How many engineers are involved in taking and verifying measurements?
- Do in-field measurements result in an excessive amount of downtime?
- Do you frequently have to discard materials due to improper fittings?
- Who in your organization would benefit from 3D scanning?
While engineers, for instance, are a natural answer to the last question, you may find that people charged with digitizing inventories or creating marketing materials would also find a 3D scanner helpful.
5 Tactics to Figure Out Which Scanner You Need
The next step is to go through the following checklist, which will help you nail down your requirements for things like materials/surfaces, part sizes, and more.
Tactic 1: Consider Throughput and Setup
How often, and where, you’ll be scanning affects operator setup and portability requirements. A scanner that yields super robust, high-quality, or complex meshes may not be suited well for travel. If your engineers or paleontologists primarily work in the field, or if you share a scanner across departments, you may need a portable device versus one used solely on a single manufacturing floor.
Tactic 2: Consider Material and Environmental Conditions
What types of materials do you scan and in what kind of environment? These factors influence the longevity and reliability of a 3D scanner. They also affect total scanning time. Think about issues like:
- Material surface (glossy, matte, dark, light, transparency, etc.)
- Extreme temperatures (heat, freezing) and swings in storage
- Environmental conditions (dust, dirt, humidity, vibration, clean room, etc.)
Tactic 3: Consider Part Size
3D scanners are amazing in their ability to capture everything from sub-millimeter-sized parts to massive items larger than 45 feet across. But not every scanner will suffice for both. Do you need one with a great deal of range or one for either end of the size spectrum? This affects acquisition speed and resolution for accuracy and quality control.
Tactic 4: Consider Accuracy and Resolution
Let’s talk more about accuracy and resolution. Your 3D scanner will output real-world parts into a digital format. The better the accuracy (feature position and size) and resolution (level of sharp detail), the more usable the mesh will be. You want to choose a scanner that will give you both of those qualities across the entire span of the object in question for successful inspection or design.
Very large objects can tolerate some degree of deviation from accuracy, whereas extremely small parts cannot. Other concerns include:
- Surface complexity and texture
- Sharpness of edges
- Text or markings
- Crack identification
- Holes and pockets
- Hole patterns
- Thin-edge surfaces
- Pins and extrusions
Tactic 5: Consider Acquisition Method
Finally, data acquisition is another key consideration. How will the operator acquire data? What training will they need to produce the quality you desire? Can you capture everything necessary to create points without frequent repositioning or lengthy scanning times? What about the field of view of the device?
The right scanner is one you can actually get results with. That differs widely when thinking about factors like:
- Touch probes
- Tripod mounts
- Robotic operation
- Single vs. multi-line modes
- Structured light or LiDAR technology
- Laser triangulation
- Desktop applications
Artec Scanners: Versatility and Accuracy
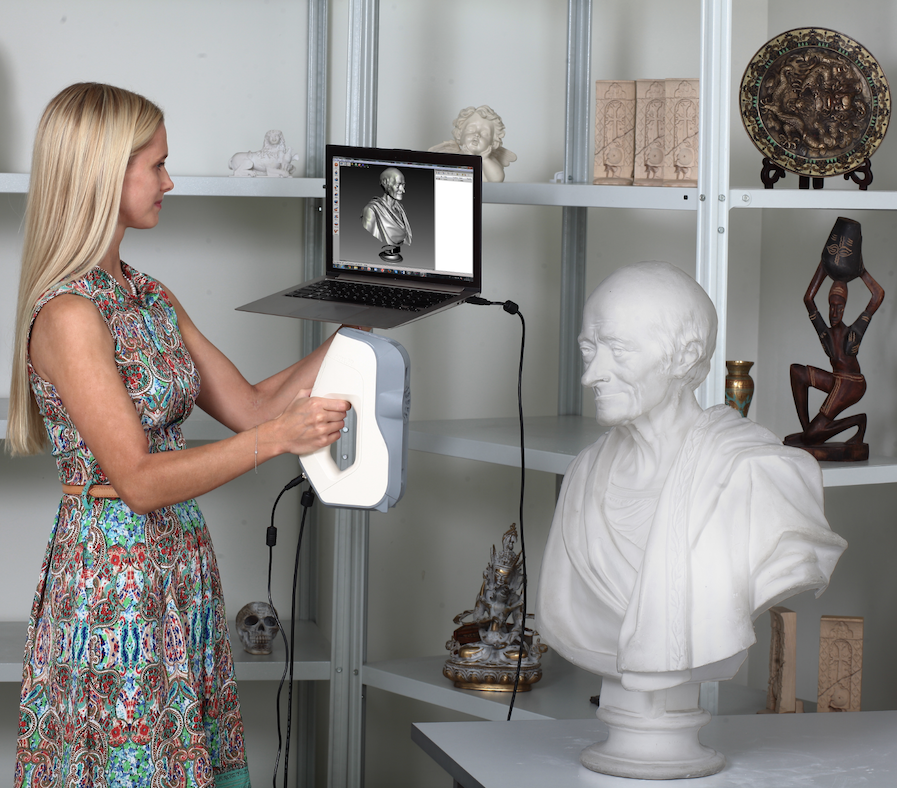

3D scanners from Artec are known for their versatility and user-friendliness. The company’s selection of portable devices means you’ll often find them in a wide spectrum of industries including Medicine, Archaeology, Construction, Education, and Forensics.
Users appreciate the ability to capture high-quality geometry and color data with a high degree of both resolution and accuracy. The Artec Leo gives you wireless portability and self-tracking algorithms — ideal for working in tight spaces. Need to scan small parts in extreme detail? The Artec Micro II might be for you, with its automated rotational bed.
Artec Studio, the maker’s premier processing software, pulls it all together. All Artec 3D scanners can work together with this software, so you can create mesh files from data supplied by multiple scanners. Artec scanners also give you robust editing and data cleanup capabilities, among other features. They’re popular for reverse engineering and inspections.
SCANTECH Scanners: Speed and Portability

When you need high accuracy and fast laser scanning at an affordable price, SCANTECH might be a good choice for your company. That’s why SCANTECH devices are often used by professionals in fields like Manufacturing, Archaeology, Automotive, Aerospace, and Restoration.
SCANTECH’s blue laser scanners capture millions of data points to produce detailed meshes, especially for objects that are traditionally difficult to scan.
The technology also lets users scan anything from a tiny airplane dash component to an entire forward fuselage with the same device.
Other features of SCANTECH devices include:
- Rapid data capture across surfaces
- Lightweight device design
- Adjustable camera and laser systems
- Minimal preparation for complex scans
Both in-field and factory floor scanning are less disruptive with the wireless scanning capability and object tracking through targets on the object or via an optical scanner.
SCANTECH devices also lets you create a scanning space with multiple trackers, so you don’t have to constantly reposition.
Download the Scanning Buyer’s Guide
Want more details to help you hone in on the right device for your organization? Grab our new 3D scanner buyer’s guide or reach out to a rep for more details.