The push for sustainability in manufacturing has led to a surge in new technologies and processes that minimize environmental impact.
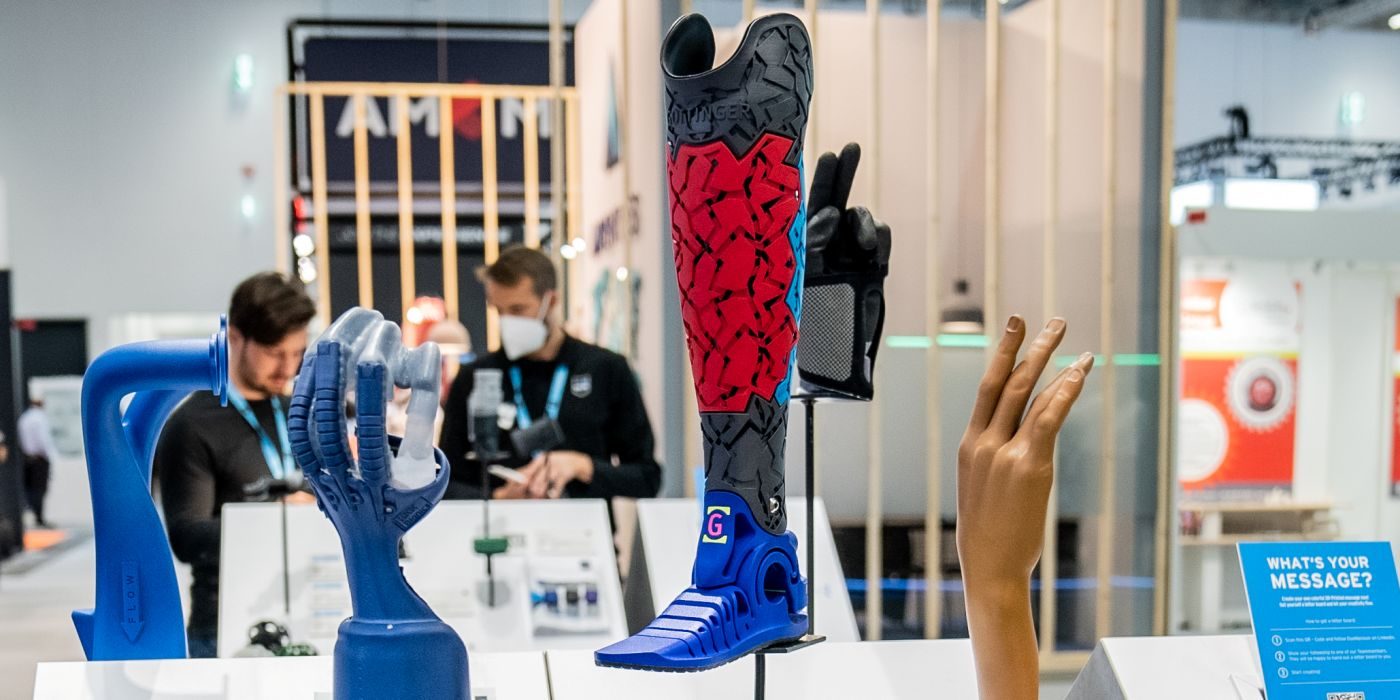
3D printing or additive manufacturing (AM) is at the forefront of this movement. HP’s 3D printing solutions are revolutionizing sustainability practices across industries.
In this article, we’ll explore how HP’s additive manufacturing technologies, materials, and design strategies drive environmental sustainability.
Using Sustainable Materials in 3D Printing Workflows
A key pillar of sustainability in manufacturing is the use of eco-friendly materials. HP has invested heavily in developing high-reusability polymers and metals that align with sustainable manufacturing goals.
Here’s how HP has refined their materials:
- Polymers: HP’s materials, like PA11 and PA12, boast industry-leading reusability rates. PA11, for instance, is made from 100% renewable carbon content sourced from non-GMO castor plants. These plants are grown in arid regions, meaning they don’t compete with food crops, making PA11 a bio-based material with minimal environmental impact.
- Metals: HP’s metal binder jetting process ensures that 100% of recovered metal powder is reused, a significant improvement over traditional methods where large quantities of material are wasted.
By enabling the reuse of up to 80% of polymer powder and 100% of metal powder, HP’s materials significantly reduce waste without compromising mechanical performance, making them ideal for sustainable production workflows.
How 3D Printing Reduces Supply Chain Waste
One of the most significant advantages of additive manufacturing is the ability to localize production, which reduces the environmental footprint associated with traditional supply chains.
Additive manufacturing allows companies to produce parts on demand, reducing the need for global transportation and large-scale warehousing. By eliminating long supply chains and reducing dependency on overseas production, companies can lower carbon emissions and cut down on packaging waste.
This shift reduces environmental impact and enhances supply chain security by reducing lead times and minimizing disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions or global pandemics.
Ways to Use Sustainable 3D Printing Designs
Design optimization is crucial in additive manufacturing, particularly when aiming for sustainable production.
Two examples are:
- Mass Customization: Additive manufacturing allows for mass personalization without the need for additional tooling. This flexibility means that parts can be tailored specifically to customer needs, reducing unnecessary production and waste associated with excess inventory.
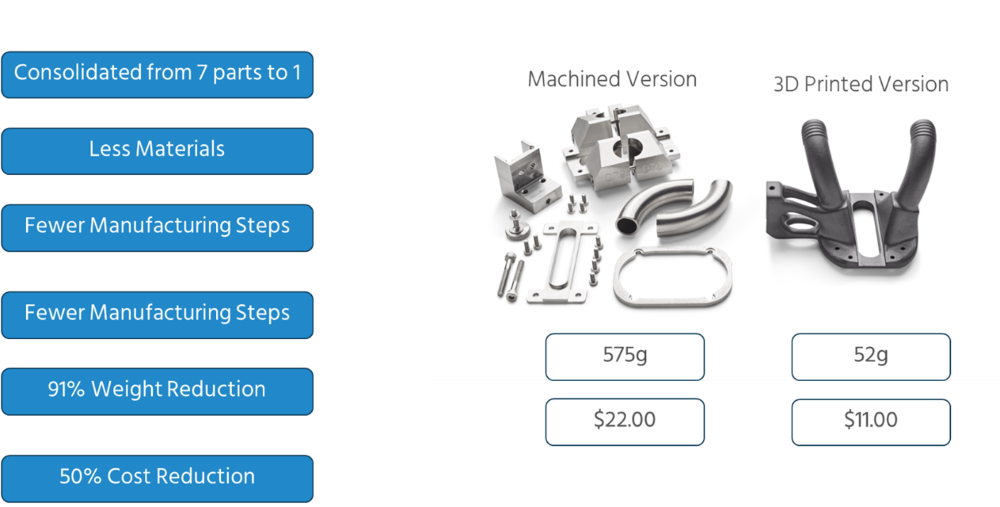
- Assembly Consolidation: Traditional manufacturing often involves the production of multiple components that are then assembled. In contrast, 3D printing allows for assembly consolidation — multiple parts can be integrated into a single structure. This reduces material use, transportation, and the need for adhesives or fasteners, leading to a lighter environmental footprint.
HP’s 3D printing technology enables highly efficient, lightweight designs that conserve materials and energy.
For instance, HP’s multi jet fusion (MJF) technology has been used to consolidate parts, reducing both cost and material usage. A specific case involved a component for HP’s large-format 2D printers, where a part that was traditionally machined from aluminum was replaced with a 3D-printed design, resulting in:
- 50% cost reduction
- 93% weight reduction
- 95x reduction in carbon footprint
These optimizations are not only environmentally friendly but also result in better performance and reduced production costs.
HP’s Environmental Impact: Design for Sustainability (DfS) Program
HP’s journey toward sustainability began long before the rise of additive manufacturing. The Design for Sustainability (DfS) program, established in 1992, focuses on minimizing the environmental impact of products throughout their lifecycle.
HP’s sustainability goals are reflected in the following areas:
- Material Efficiency: HP is committed to reducing the use of harmful chemicals, increasing the efficiency of materials, and switching to recycled or certified sustainable fiber for packaging.
- Packaging Innovations: By reducing the size and complexity of packaging and eliminating hard-to-recycle plastics, HP has significantly improved the recoverability of materials, driving circularity.
- Circularity Initiatives: HP’s focus on circular design principles includes take-back programs, where used powders and end-of-life parts are collected, processed, and reintegrated into the production cycle.
Through initiatives like these, HP is reducing its environmental impact while encouraging sustainable practices across the industry.
Designing for Energy Efficiency and Emissions Reductions
HP’s 3D printing technologies are designed to optimize energy consumption and reduce emissions compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Here’s how:
- Energy Efficiency: HP’s Jet Fusion and Metal Jet systems are highly efficient, consuming around 30 watt-hours per cubic cm for the entire production process (pre-processing, printing, and post-processing). This is a fraction of the energy used in conventional methods like injection molding or laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF).
- Lower Emissions: HP’s enclosed printing systems offer cleaner production environments and help minimize process-related air emissions, making them suitable for production in facilities aiming to meet strict environmental standards.
A recent study by AM Power found that metal binder jetting, one of HP’s key technologies, can reduce environmental impacts by up to 69% compared to L-PBF and 62% compared to injection molding, particularly in short- to medium-run productions.
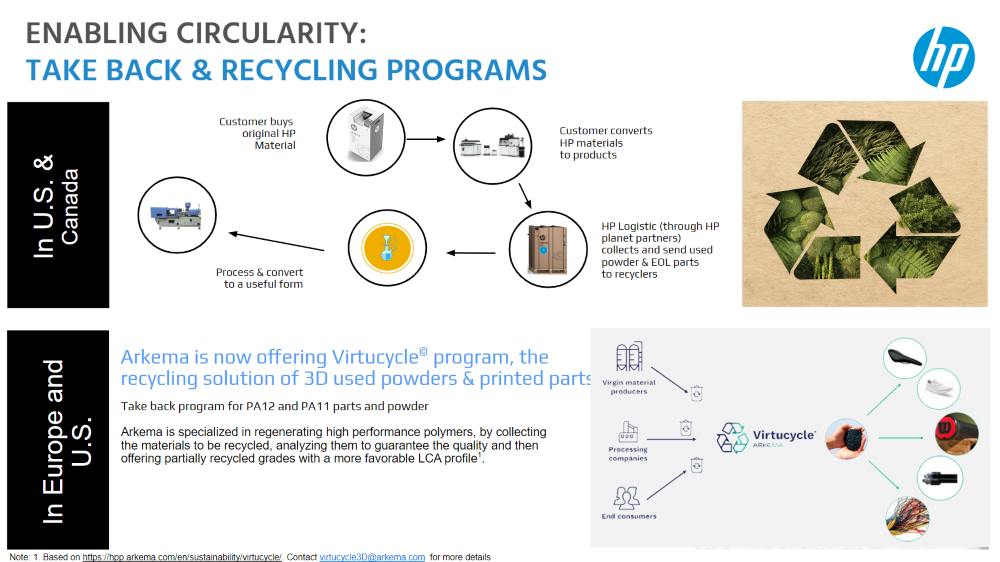
Enabling Circularity Through Take-Back and Recycling Programs
A major focus for HP is enabling circularity — designing products and materials that can be continually reused or recycled. HP has partnered with Arkema’s Virtucycle© program to create a comprehensive recycling solution for PA11 and PA12 powders and printed parts.
Through these programs, customers can send back used powder and end-of-life (EOL) parts, which are processed and converted into new materials with the same high performance and a more favorable lifecycle assessment (LCA) profile.
This approach ensures that materials stay in circulation, reducing the need for virgin resources and decreasing overall waste.
Case Study: Sustainable 3D Printing at HP
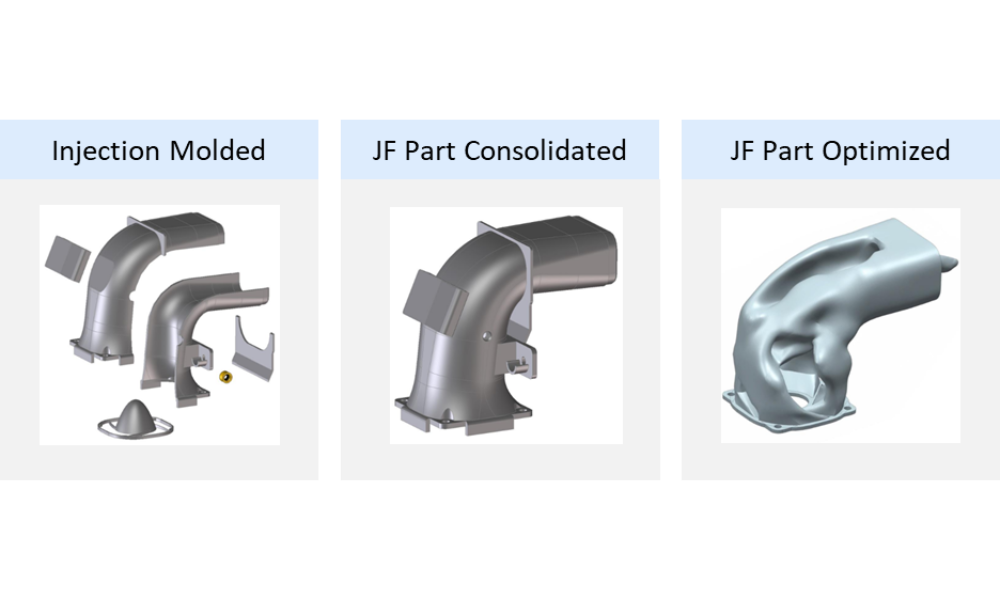
One of the standout examples of HP’s commitment to sustainable design is its HP Jet Fusion air duct. The duct plays a crucial role in cooling the printer head pens and was optimized using 3D printing and convergent modeling.
The design, initially composed of six parts, was consolidated into a single, optimized part using HP’s 3D High Reusability PA11. This change resulted in:
- 34.3% cost reduction
- 22.3% flow improvement
By leveraging the flexibility of 3D printing, HP was able to not only improve the functional performance of the part but also reduce its environmental impact.

What’s the Future of Sustainability in 3D Printing Look Like?
HP’s 3D printing technologies and materials are paving the way for more sustainable manufacturing practices. Through material efficiency, energy optimization, design innovation, and circularity initiatives, HP is significantly reducing the environmental footprint of additive manufacturing.
As the demand for sustainable solutions grows, HP continues to set the standard for eco-friendly production in additive manufacturing, offering tools and resources that not only improve production efficiency but also promote a more sustainable future.
By integrating sustainability into every stage of the manufacturing process — from material sourcing and design to production and recycling — HP is driving the industry toward a more responsible and environmentally conscious future.
Explore our additive manufacturing blog section to stay up to date with the latest in 3D printing or take a dive deep into how HP 3D printing works.
Contact us today if you have any questions!
Watch the Webinar
Learn more about this topic from our 3D printing experts. We explore greener options with 3D printing in our webinar, Harnessing 3D Printing for Sustainable Manufacturing Solutions.