Have you ever received an STL file from a customer or colleague and been asked to work with it in SOLIDWORKS? Or have you ever received data from a 3D scanner? If so, then you have probably been left wondering, “How do I work on this in SOLIDWORKS and why can I not use my regular tools and features?” In today’s article, we are going to look at three different tool sets that can be used to work with mesh data.
Mesh data is saved in a variety of file formats, the most common being STL, though you may have run across a number of others (.obj, .ply, .3mf, .amf). These file types generally save geometry as a series of connected triangles (also known as tessellations) and usually cannot be edited by standard SWX features.
The Quick Breakdown
Mesh Modeling Tools
Availability: All versions of SOLIDWORKS
Capabilities: Reference vertices of mesh triangles, boolean operations (add/subtract/common), extract primitive surfaces and curves
ScanTo3D
Availability: SOLIDWORKS Professional
Capabilities: Edit/clean-up mesh, Extract organic or prismatic surfaces and curves, perform deviation analysis
Geomagic For SOLIDWORKS
Availability: Separately purchased SOLIDWORKS Add-in
Capabilities: Create mesh from Scan Data, Advanced mesh editing and clean-up tools, Advanced surface and curve extraction, perform deviation analysis
SOLIDWORKS Mesh Bodies
In SOLIDWORKS 2018, mesh modeling functionality was added to all versions to allow some utilization of mesh files. While the amount you can truly edit a mesh body is limited, it does give you great options for utilizing mesh data in standard SOLIDWORKS parts or assemblies. The Mesh Modeling tab of the CommandManager (found by right-clicking a current CommandManager tab and selecting Mesh Modeling from the list) collects all of the tools that can be used to manipulate mesh data.
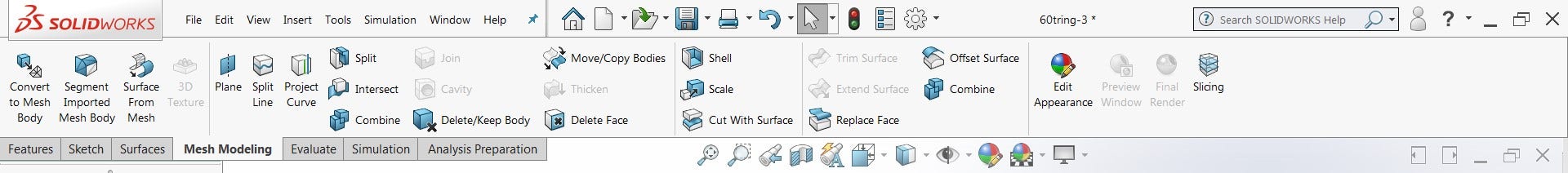
Some tools may be familiar, such as Move/Copy Body and Scale, while others are specific to Mesh Modeling such as Surface from Mesh or Slices. Even without using any special tools or features, SOLIDWORKS can now reference mesh geometry directly for sketch relations, allowing you to “trace” the mesh or build geometry around mesh bodies.
Surface From Mesh can be used to extract primitive surface bodies (planes, cylinders, cones, spheres) from a mesh to be used as a reference or as part of your design.


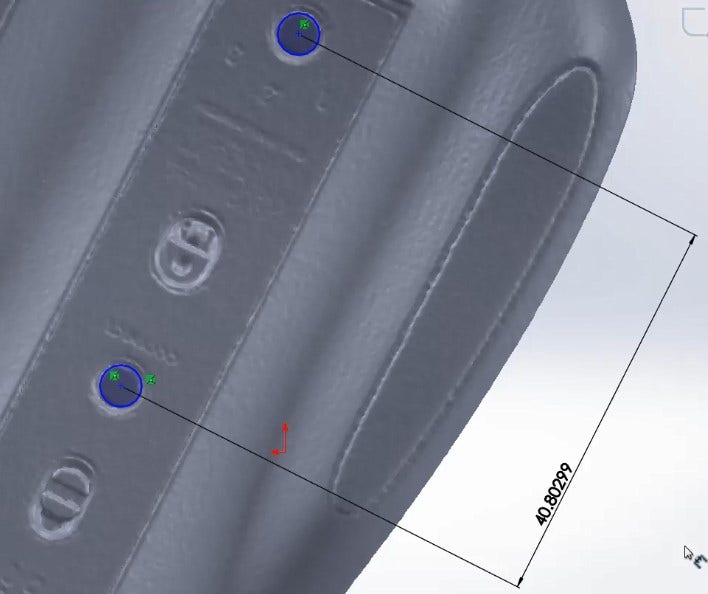
The slicing tool extracts cross sections directly from the mesh body for getting profiles and references to organic and complex shapes.
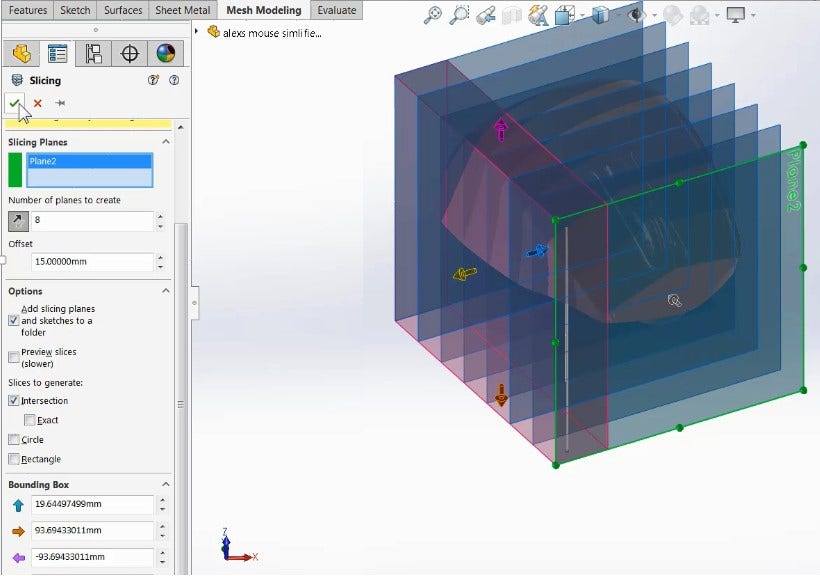
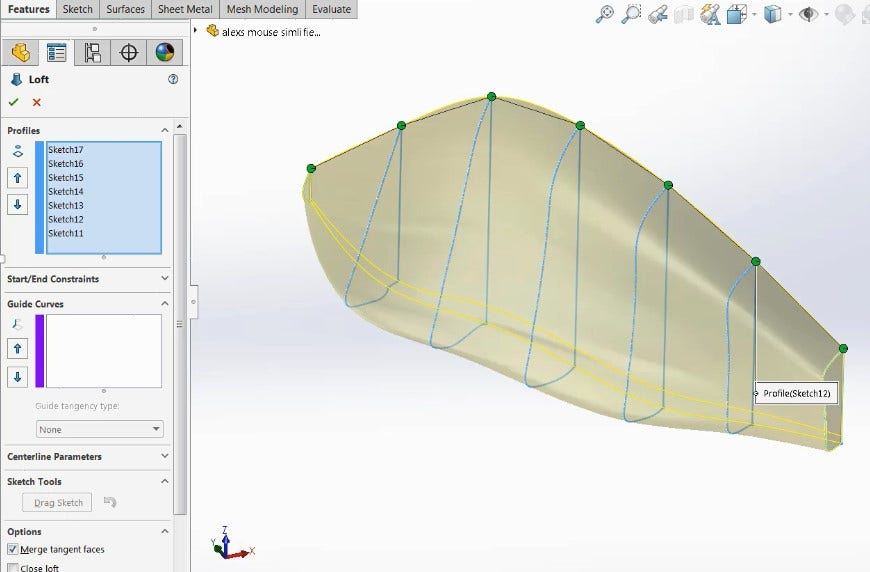
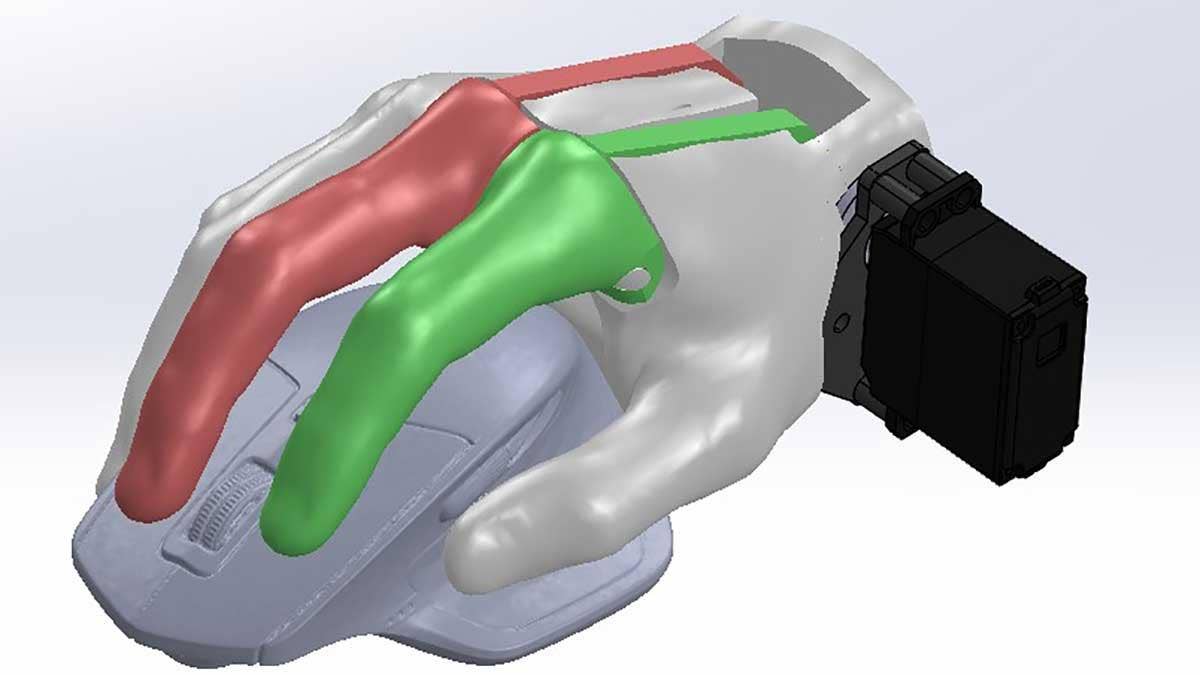
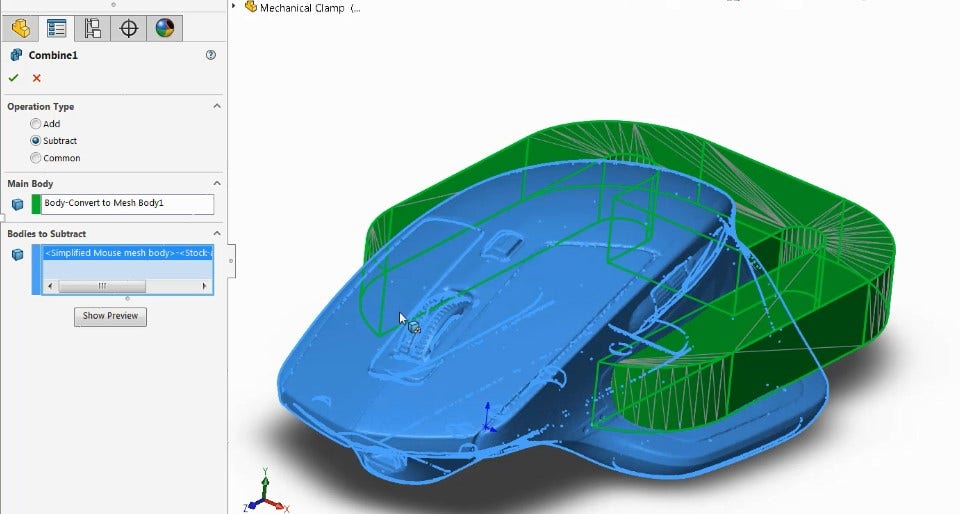
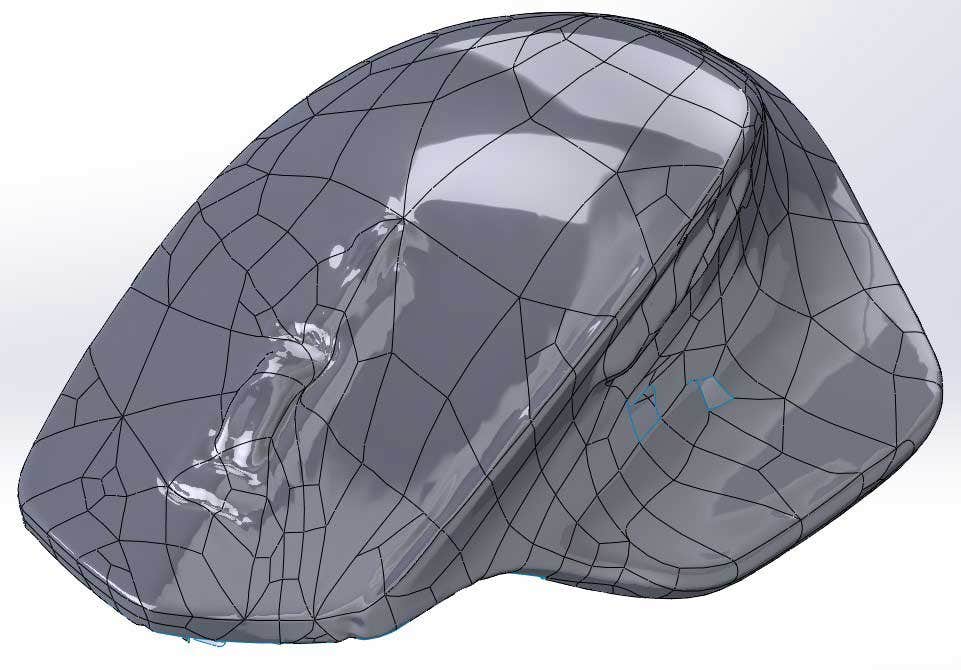
One of my favorite options is being able to use Convert to Mesh Body (used to convert standard solid bodies to mesh) and Combine to perform Boolean operations. This approach can be used to modify mesh bodies, such as hollowing out this mouse scan for printing.
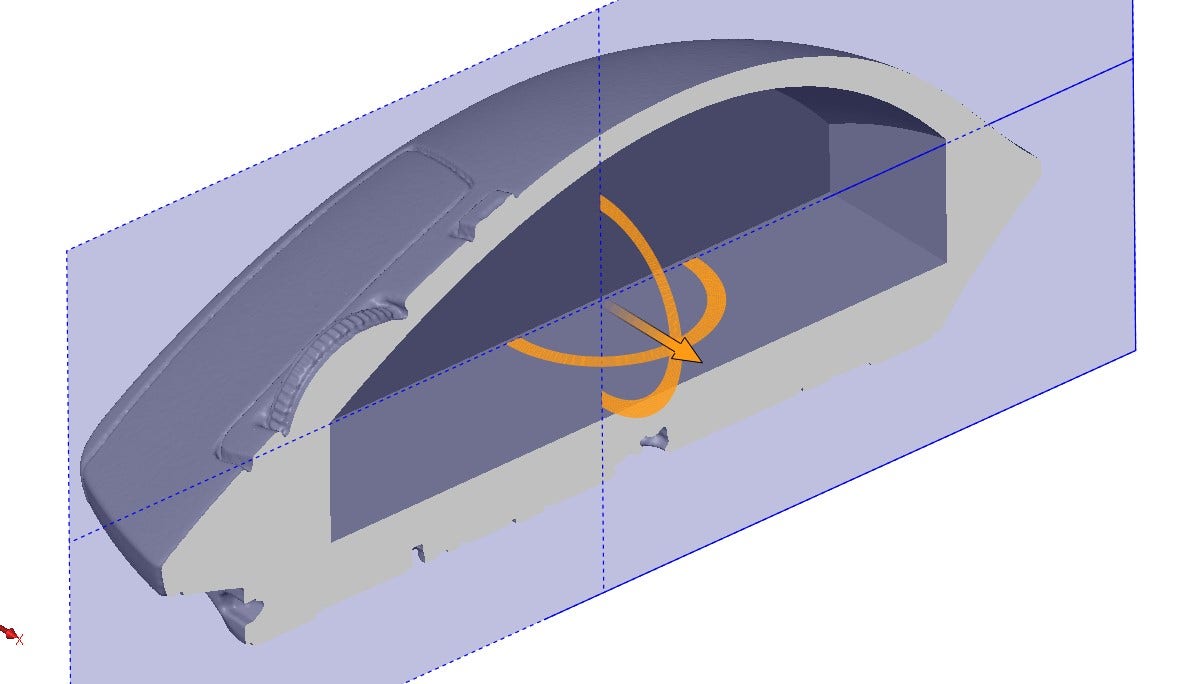
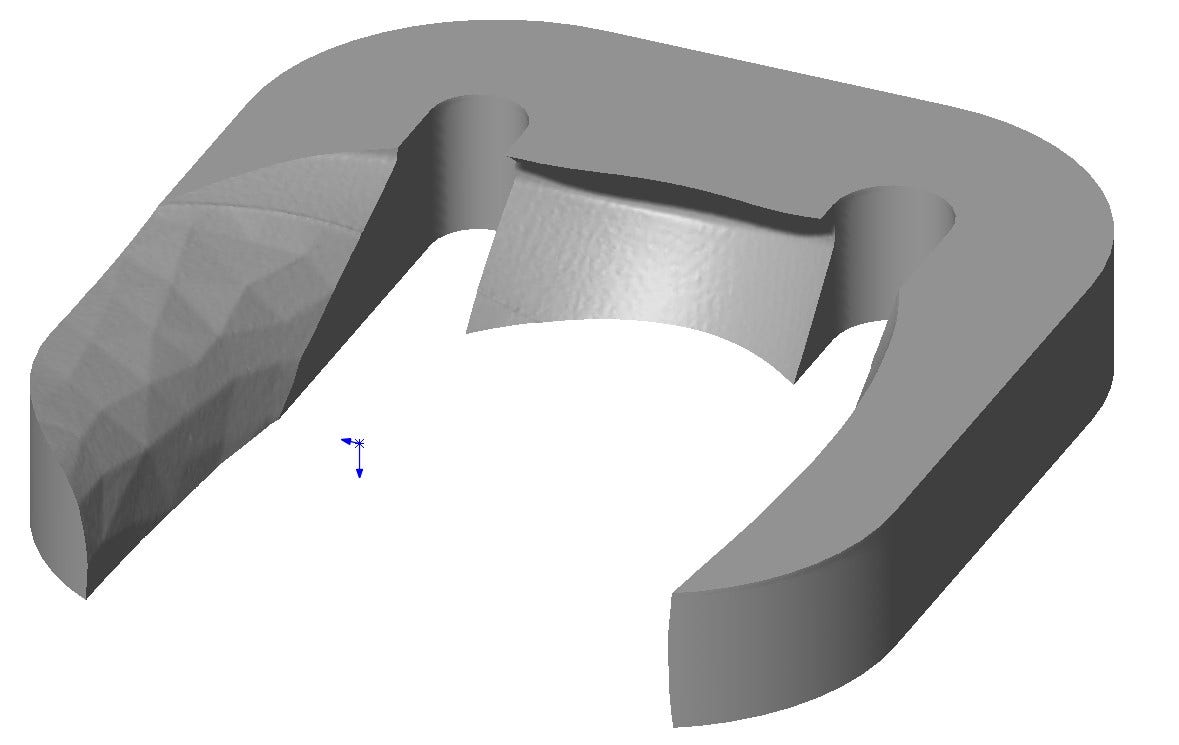
It can also be used to integrate the mesh data into an existing design as seen below in the “gripper” device used to hold the mouse. One thing to note is that once something is converted to a mesh body, normal features can no longer affect it so make sure to use the Combine feature near the end of your design!
SOLIDWORKS ScanTo3D
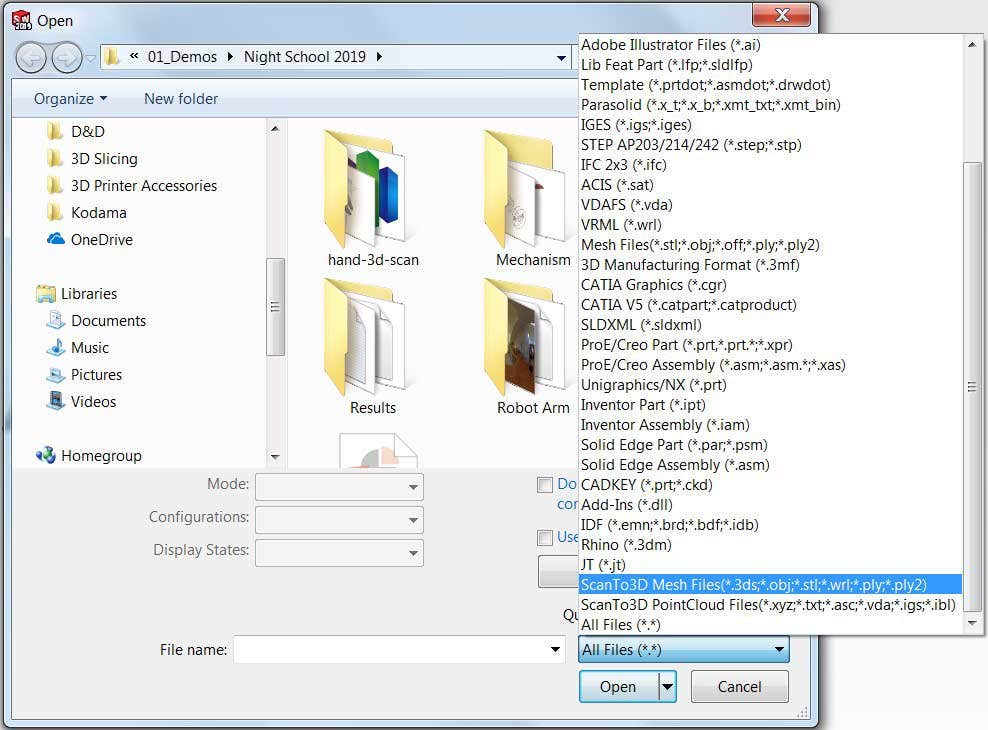
ScanTo3D is a SOLIDWORKS Professional add-in and its main benefits over the Mesh Modeling tools is that you have the ability to edit/clean up mesh files and generate surface patches for organic or complex shapes.
ScanTo3D uses its Mesh Prep Wizard to move, smooth out, fill in holes or even delete sections of mesh bodies. The Mesh Prep Wizard walks you through each step, providing applicable tools, allowing you to edit the mesh file before using it in your design. This is very helpful when receiving 3D scan data that may have artifacts from scanning such as extraneous detail, holes, or rough surface quality.
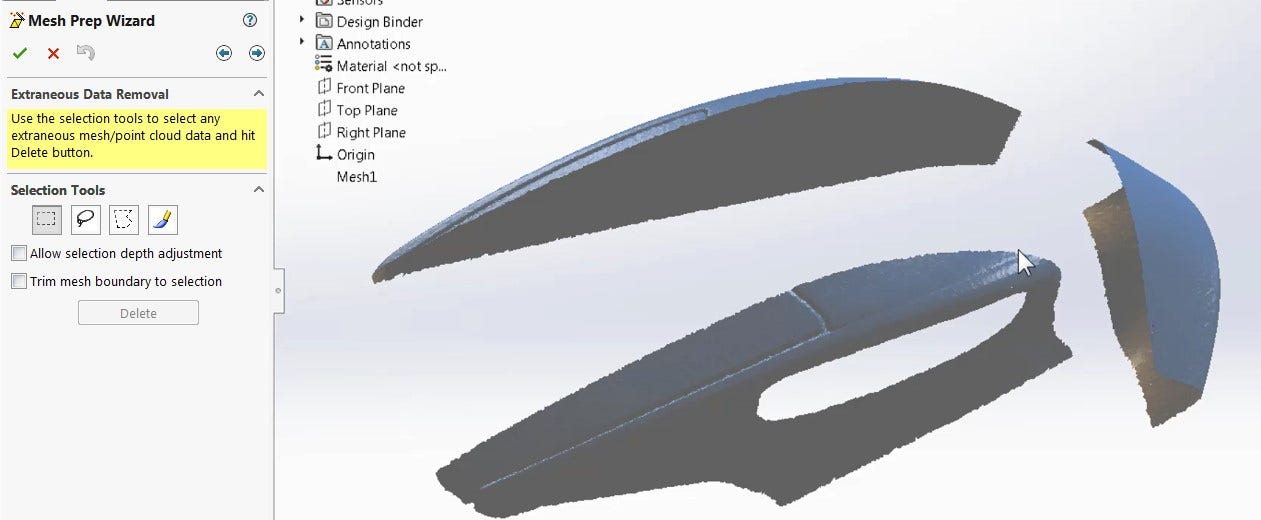

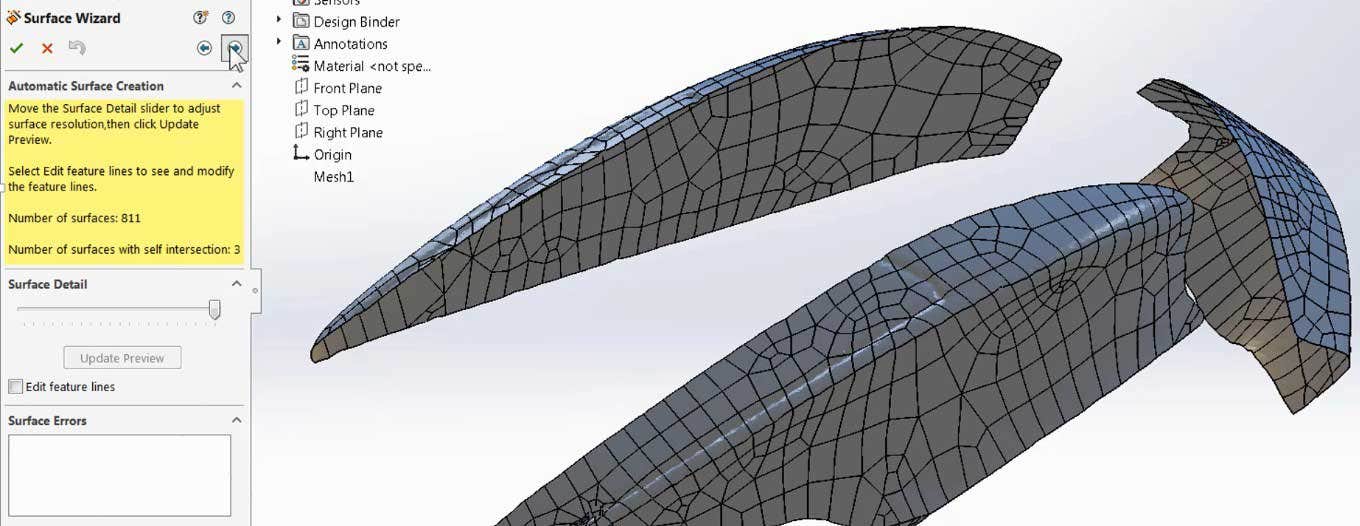
ScanTo3D can also be used to generate surface patches directly from the mesh data with the Surface Wizard. Though commonly used for organic or complex geometry, prismatic geometry such as cylinders, cones and planes can be extracted as well. For best results, the Mesh Prep Wizard should be used to reduce the mesh data to only the areas of interest. These surfaces patches are standard SOLIDWORKS surface bodies instead of mesh, so you can then utilize all of the standard sketch and feature tools.
Geomagic for SOLIDWORKS
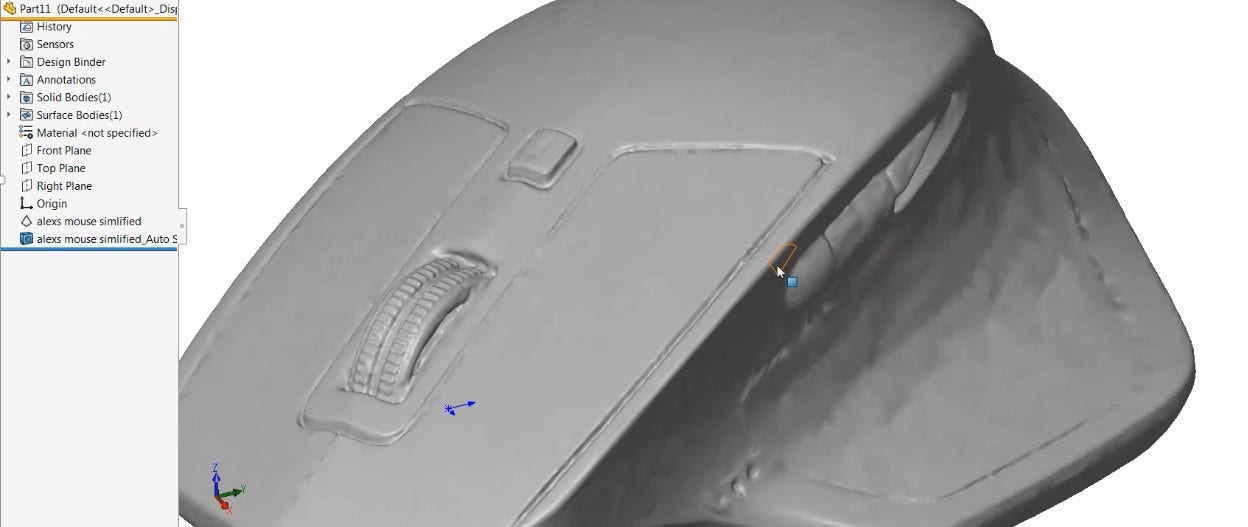
The separately purchased Geomagic for SOLIDWORKS add-in is a true reverse engineering tool and is our recommendation if you are working with mesh data regularly. The Geomagic add-in provides a much larger range of control when editing and cleaning up mesh data as well as when generating standard SOLIDWORKS Geometry with Auto Surfacing, Extract Freeform and more common tools such as Cross Sections and Primitive Surface extraction. The results that you can get from these tools are not only of higher quality, but also much faster and require less input from you. In the image below you can see how well the Auto Surface tool can generate a solid body from good scan data, this one was done without cleaning up the mesh or adjusting any settings from default.

In this article, we have covered three different ways that SOLIDWORKS users can utilize mesh data in their designs. The Mesh Modeling tools, available to all users, are a quick way to reference mesh data with sketch relations or when utilizing Boolean operations to make small changes to the mesh bodies and add the mesh data directly to an existing design. ScanTo3D, for SOLIDWORKS Professional users, will increase those capabilities by giving you tools to edit the mesh data and extract surface patches for organic geometry. Finally, the Geomagic for SOLIDWORKS add-in, can perform all of these functions faster and with more control and accuracy, making it the best option for users who regularly work with mesh data.
For more information on SOLIDWORKS and Geomagic software or if you have any questions, contact us at Hawk Ridge Systems today. Thanks for reading!